Energy for Life
What Is the Difference between Oxidation and Reduction Reactions?
Redox Reactions
Redox reactions are used to store and release energyglossary term (opens in a new window) in biological systems. Electrons can be moved from a lower energy state in one atom to a higher energy state in another atom; this serves to store energy. Electrons can also move from higher energy states in one atom to lower energy states in another, thus releasing energy. The movement of electrons from one atom to another changes the oxidationglossary term (opens in a new window) number of both atoms. Any chemical reaction that changes the oxidation number of atoms is called a redox reactionglossary term (opens in a new window).
The term redox is a combination of the terms reductionglossary term (opens in a new window) and oxidation. Reduction is the gain of electrons, which decreases the oxidation state of the atom or ion. In reduction, the potential energyglossary term (opens in a new window) of electrons is increased; this stores energy. Oxidation is the loss of electrons, which increases the oxidation state of the atom or ion. In oxidation, the potential energy of the electrons is decreased, which releases energy. Oxidation and reduction reactions often occur together as one atom gains an electron from another atom. This reaction is called a redox reaction because one atom or ion has been reduced from the oxidation of another atom or ion.
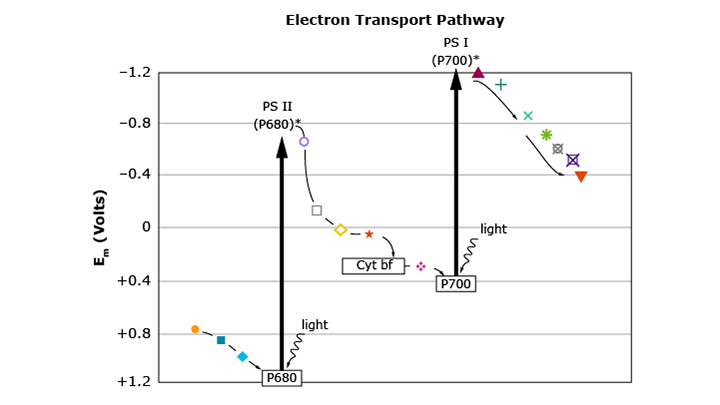
In living things, energy is usually stored and released through redox reactions. For example, in photosynthesisglossary term (opens in a new window) carbon dioxide is reduced to make sugars, and water is oxidized to form oxygen. Chemical reactions like this occur in many small steps. Each step is a small redox reaction.
Teacher Note: Misconception
Students may equate the use of energy with burning. Although burning (combustion) is an oxidation reaction, it releases heat and other forms of energy very rapidly. To avoid the damage associated with burning, cells have evolved metabolic pathways that oxidize food through a series of small steps.
Teacher Note: Practices
In this item, students explain why the energy of an electron decreases as photosynthesis uses the energy in the electron to reduce carbons. They construct, use, and present a written argument based on data and evidence. Use the Twenty Questions strategy to help them understand the information presented in the graph. As they examine the graph, have them pose questions about the graph. The Twenty Questions strategy is found on the Professional Learning tab. Click on Strategies & Resources, then click on Spotlight on Strategies (SOS). Now click on Inference and Prediction, then click on Spotlight on Strategies: Twenty Questions.