Plant Reproduction
Thinking about Pollinating Plants
Have you ever seen a field of wildflowers with butterflies fluttering back and forth? Such a scene is renowned for its beauty. The beauty, however, is not just in the eye, but also in the relationship between plants and animals; you might not know it, but the butterflies and the flowers surrounding them work together for a very important function. The vast majority of flowering plants depend upon arthropods, reptiles, birds, or even mammals for their reproduction, and it is the animals that move the pollenglossary term (opens in a new window) from flower to flower. These relationships are so important that the very structures of the plants, and their pollinators, have evolved for the purpose.
Will that field of wildflowers cause you to sneeze and have watery eyes? Perhaps you, or someone in your family, experiences “cedar fever” or “hay fever.” For many people, the spring is heralded by seasonal allergies. Spring is the time when most plants reproduce. Plant reproduction often involves pollen, and this powdery material can bring symptoms such as a runny nose and itchy eyes to an allergic person. Imagine almost every plant around you releasing pollen within a short period of time. It is no wonder that the amount of pollen in the air is so high that many people are miserable for weeks during this time of year.
Do your favorite snack foods include fruits, nuts, or seeds? Seeds are often the products of plant reproduction. Seeds come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Sometimes, seeds come in a form that is not readily identifiable as a seedglossary term (opens in a new window), such as the kernels on an ear of corn, for example. The seeds of some plants are found inside fruits or nuts. What types of seeds are familiar to you?
Explain Question
How are male and female gametes transferred during reproduction in different types of plants?
Teacher Note
Use this formative assessment to help students begin to understand relationships between cause and effect in biological systems. This activity provides feedback on prior knowledge of pollination. This activity would work well with paired student discussions.
Before You Begin
What do I already know about plant reproduction?
Teacher Note
Use individual student responses on this formative assessment to provide feedback on prior knowledge of this topic. The assessment will determine if students can identify angiosperms as flowering plants and if students understand the fundamental differences in reproduction between flowering and nonflowering seed plants.
Teacher Note
This formative assessment examines prior knowledge of plant reproduction, specifically the importance of seed production to the variation and spread of plants across the globe. Use this activity as class discussion to begin the lesson.
Teacher Note
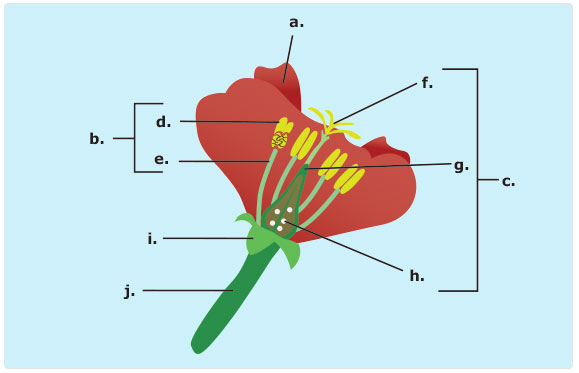
This formative assessment activity is intended to provide the teacher with feedback on prior knowledge of this topic. Its main focus is to determine whether students know the structures of plants related to reproduction. This activity can be completed individually.
Teacher Note
This formative assessment activity will provide some feedback on potential student misconceptions on plant reproduction. Students who choose A do not know that some plants self-fertilize. Students who choose D may not realize that fungi produce spores or that fungi are not plants. Students who choose F may not realize that fruit contains seeds and is a result of sexual reproduction Students who do NOT choose B and/or C may have no prior knowledge of plant reproduction. Students who do NOT choose E may think that all plants have separate male and female sexes. This activity can be completed as a class discussion to review/introduce the meaning of the terms and relate them to reproduction of various life forms.
Find out More About...
- the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction
- the main structures of plants
- the four main categories of plants
- the process of photosynthesis
Lesson Questions
- What are the methods of asexual and sexual reproduction in plants?
- What are the reproductive structures in plants?
- What are the processes of pollination and fertilization in plants?
- What is the influence of light on plant growth and development?
- What are plant responses to gravity and touch?