Describing Populations
How Are Age Structures Created?
Age Structure Diagrams
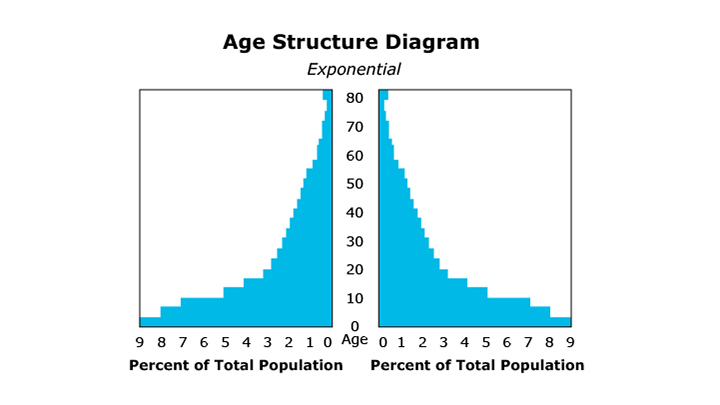
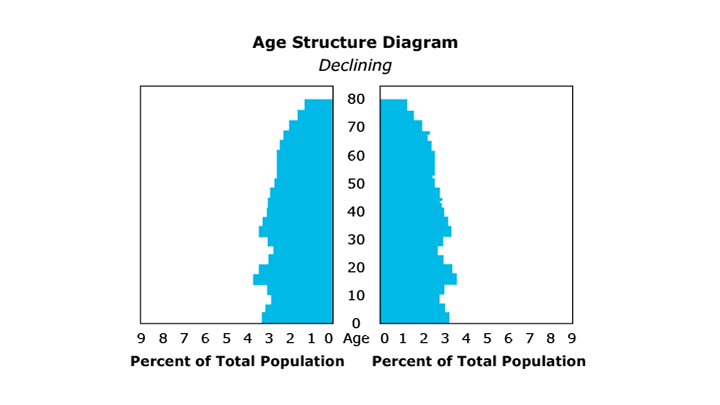
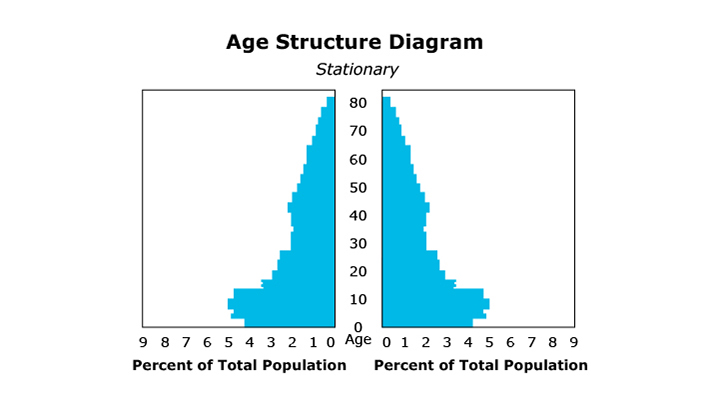
One demographic measure of a populationglossary term (opens in a new window) is an age pyramidglossary term (opens in a new window), or age structure diagram. An age pyramid is a diagram, often pyramid-shaped, that shows the age distribution of a population. This diagram can be used to determine if a population’s size is growing, shrinking, or remaining relatively constant.
Teacher Note: Connections
When examining age structure diagrams, students should understand that empirical evidence is required to make claims about the specific causes of population changes. To give students context for age structure diagrams and cause and effect relationships, organize them into small groups and assign each group a country. Students can use online resources to research the population of the country. For example, the United Nations Population Division has graphs showing population trends in all countries, including population pyramids. Instruct groups to describe their country’s age structure diagram in 1950, 2015, and 2050. Then, instruct them to write a list of factors that could contribute to the changes they observe and how they could determine whether each of the potential factors they list could have caused the changes. If necessary, review the difference between cause and correlation with students.
Constructing an age pyramid begins with a basic census of the population. Each organism’s gender and age are determined and plotted on a graph. Males are graphed on the left, females on the right of the diagram. The genders of the individuals are graphed because the diagram will be used to determine potential growth of the population. If one gender is much higher in number it can affect the growth rate. The number of females in particular has a greater effect on the population growth rate.
The age structure of the population is used to forecast the future population size. If a population has many more young individuals than older individuals it will likely grow in size over time. As the young individuals reach sexual maturity they will begin reproducing and increasing the population size.
If the number of young individuals is about the same as the number of individuals of reproductive ages, the population size will remain stable. If the number of young individuals is less than the number of individuals of reproductive ages, the population will decrease in size. Average reproductive rate must also be considered. If each individual produces a single offspring, the population will remain stable. If the number of offspring per individual averages less than one, the population will decline.