Cellular Respiration
Applying Cellular Respiration
Why do muscles sometimes get sore when we exercise? What has this got to do with cellular respirationglossary term (opens in a new window)?
Many animal cells use a form of fermentationglossary term (opens in a new window) that produces lactate. This occurs in conditions of reduced oxygen availability. For example, during vigorous exercise, an athlete’s muscles need more ATP. The muscle cells may not be able to get enough oxygen to supply this ATP through aerobic respirationglossary term (opens in a new window). Instead, they temporarily switch to using anaerobic respirationglossary term (opens in a new window). This produces lactate which builds up in the muscles. When the athlete stops exercising, and an adequate amount of oxygen becomes available, this lactate will be converted to pyruvate and then oxidized in aerobic respiration.
Muscle soreness during or after exercise may in part be caused by the buildup of the lactate in your muscles. When the buildup reaches a certain point, a burning sensation can be felt, and the muscles may actually lock up or cramp. However, this accounts only for the temporary soreness immediately after exercise since the lactate is usually converted into pyruvate minutes after exercise has stopped. Longer term muscle soreness is caused by damage to muscle fibers and other parts of the muscular system. These microtraumas cause inflammation and pain that can last for days. In addition to the injured fibers, increased blood flow to the muscles causes muscle tissues to swell. This causes pressure that stimulates pain receptors. So painful muscles often have microscopic tears and are swollen. The fix for longer term muscle soreness is quite simple: if you stretch and warm up properly before the activity and gradually increase the endurance and strength of your muscles, you will not get so sore.
STEM and Cellular Respiration
Humans benefit from fermentation in many ways. Bacteria and yeast produce some of the foods people eat through fermentation. One common type of lactic acid-producing bacteria is Lactobacillus bulgaricus. These and other lactic acid bacteria ferment milk to produce yogurt. Sauerkraut and kimchi are other foods produced by the fermentation of vegetables.
Brewers also make use of ethanol fermentation in yeast. All alcoholic beverages are produced by the fermentation of fruits, grains, and vegetables by yeast. For bakers, yeast is an important ingredient in bread dough. One of the byproducts of the fermentation reaction is carbon dioxide ( ). The basic formula for the ethanol fermentation reaction is:
A unique enzyme catalyzes this reaction in which NADH is converted to NAD+. The chemical formula for ethanol is . The carbon dioxide gas given off during fermentation is necessary for bread to rise.
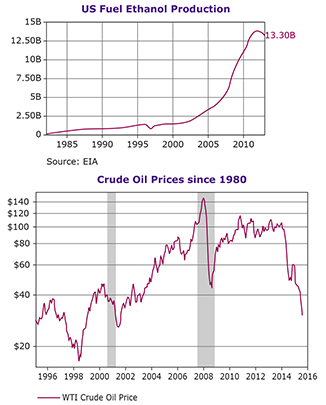
Another important use for ethanol fermentation is in the production of ethanol as an energy source. In the United States, corn is the primary crop used for ethanol production. Other countries, such as Brazil, make ethanol mainly using sugar from sugar cane. The ethanol produced is a biofuel and can be used as an alternative energy source.
Teacher Note
Use this as a formative assessment to determine whether students can make connections between the process of fermentation and the production of ethanol to the wider economy, oil production technology and world food supplies.
-
<div tinymce="true" use-dimensions="false">Describe the trends in oil price and ethanol production since 1990. Include in your answer any relationships that may exist between them.<br></div>Describe the trends in oil price and ethanol production since 1990. Include in your answer any relationships that may exist between them.Press Space or enter key to Enter Text
-
<div tinymce="true" use-dimensions="false">Suggest why there been a decline in ethanol production in the United States since fracking for oil became common practice.<br></div>Suggest why there been a decline in ethanol production in the United States since fracking for oil became common practice.Press Space or enter key to Enter Text
-
<div tinymce="true" use-dimensions="false">If ethanol production rises, what do you think would happen to food prices? How will this impact people in the developing world? Explain your answer.<br></div>If ethanol production rises, what do you think would happen to food prices? How will this impact people in the developing world? Explain your answer.Press Space or enter key to Enter Text