Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
What Are Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis?
The Formation of Sperm
In sexually reproducing organisms, males contribute sperm and females contribute eggs. The process of forming sperm is called spermatogenesisglossary term (opens in a new window). Cells in a male organism called spermatogonia produce sperm. The spermatogonia arise from primary germ cells that undergo cell division. During mitosisglossary term (opens in a new window), one daughter cell remains a spermatogonium. The other becomes a spermatocyte, which eventually becomes sperm.
Each primary spermatocyte undergoes meiosisglossary term (opens in a new window) I, resulting in two secondary spermatocytes. The secondary spermatocytes undergo meiosisglossary term (opens in a new window) II and cytokinesis. Two spermatids, or young spermatozoa, are produced from each secondary spermatocyte. The spermatozoa develop into mature sperm cells for use in reproduction.
The Formation of Eggs
The process of oogenesisglossary term (opens in a new window), or egg formation, in a sexually reproducing female is somewhat more complex than spermatogenesis. However, like spermatogenesis, the cell that results in the formation of an egg arises from a primary germ cell, called an oocyte, that undergoes cell division to produce a haploid cellglossary term (opens in a new window). This haploid cell is called an ovum, or egg.
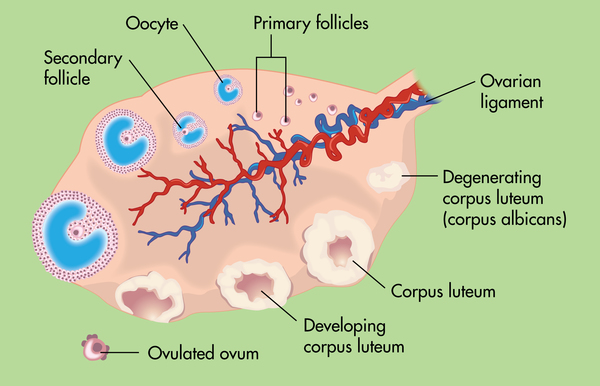
The ovarian cycle in women carries their bodies through the steps necessary to mature and release an egg cell. A normal cycle follows a series of steps.
Day 1: The hypothalamus in the brain reacts to low levels of estrogen in the blood by stimulating the anterior pituitary gland to release follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). This hormone causes several primary follicles in the ovary to develop and form secondary follicles.
Around Day 9: Only one healthy secondary follicle remains, with the rest having undergone degeneration. As the follicle grows, it releases large amounts of estrogen. As a result, estrogen levels in the blood dramatically increase. Once reaching a certain level, the hypothalamus reacts to the increased estrogen by triggering a surge of luteinizing hormone (LH).
Around Day 14: The secondary follicle develops a tertiary follicle in response to the burst of LH. Recall that the oocyte undergoes meiosis. The development of this tertiary follicle occurs after the first meiotic division of the primary oocyte. The burst of LH causes the follicle to break open, releasing the egg in a process called ovulation. The empty follicle that is left behind is now called a corpus luteum.