Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
What Are Some Examples of Aneuploidy, Monosomy, and Trisomy?
Aneuploidy and Monosomy
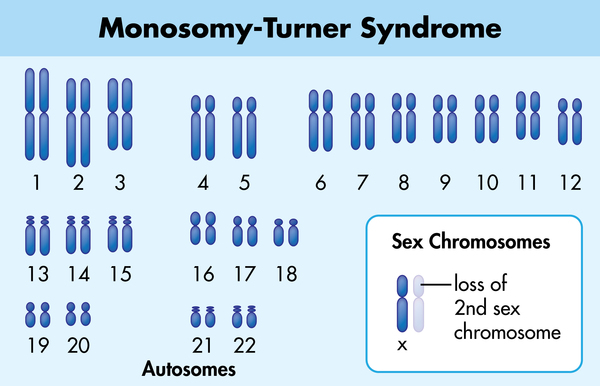
Recall that aneuploidyglossary term (opens in a new window) is a condition in which an individual inherits an abnormal number of chromosomes. Turner Syndrome is a sex-linked condition caused by monosomyglossary term (opens in a new window). A female with Turner Syndrome has one X chromosome instead of two. The resulting symptoms include incomplete development during puberty, short height, a broad chest, and infertility.
Aneuploidy and Trisomy
Klinefelter Syndrome is a sex-linked disorder found among males. As a result of non-disjunction, males receive an extra X chromosome (XXY). Small testes, enlarged breasts, other feminine body characteristics, and sterility are the typical characteristics of Klinefelter Syndrome.
Probably the most common example of trisomyglossary term (opens in a new window) Down Syndrome (trisomy 21). This disorder occurs when an offspring receives an extra copy of chromosome 21. Down Syndrome affects normal brain and body development in a child.
Another example of trisomy is Patau Syndrome (trisomy on chromosome 13). This condition results in serious eye, brain, and circulatory disorders, as well as a cleft palate.
Teacher Note: Practices
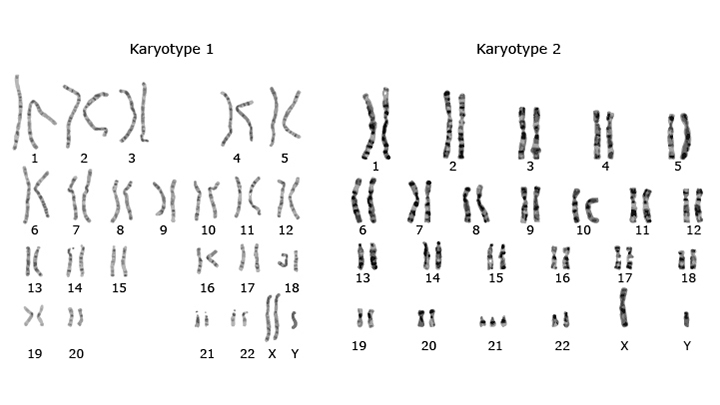
In this item, students apply what they have learned in the last two Explore sections as they analyze and interpret data using tools, technologies, and/or models (e.g., computational, mathematical) to make valid and reliable scientific claims about two human karyotypes. Extend this item by having students draw sketches to show how non-disjunction results in each of the two chromosomal abnormalities represented by the two karyotypes.